Pre-requistie: Read introduction to Workflow Model
Workflow Modeler GUI
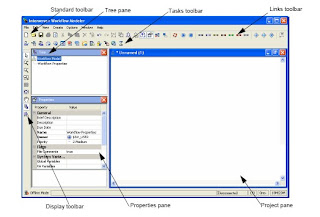
- Toolbars: Provide acess to commonly used features. All features are available through the menu system.
- Tree: Provides a method to quickly select any object (model, task, link, etc) by name. The selected object is highlighted in the digram.
- Properties: Display the property settigns for the currently selecteds object, and enables modification of property values if it is a read/write property
- Project pane: A visual representation of the workflow model. Using the toolbar, user can select new types of objects, drop it on the project pane and select the object to set their properties.
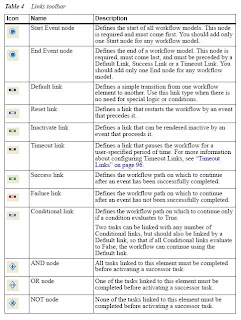
Note
- All object names must be unique
- Link names are used as transition button labels
- Some object names are used as labels on UI form e.g. user, group and metadata task. ii) links with user, group, review or metadata predecessor
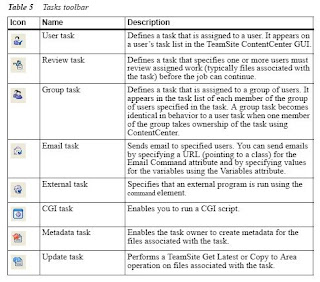
Review Task & Links
- Must have one sccess and one failure link
- May have additional default links, which will appear as additional transition options
- Success and failure link can have any name
- Use available groups and/or available user to define sets of possible reviwers for this task
- Then use Available Reviews to define the actual selection list of reviwers, which is use to generate a selection list on the job instantiation form
- Number of reviewers must be define in design time
- Use the Label and Description field to configure the form appearance of this select list
Group Task
- Have Shared By property instead of an owner property. So enter a set of users and groups to send this task to.
- One of them will take ownership and perform the task
Metadata Task
- Use to display the metadata input form but appearance will depend on its configuration setting.
- User then enters a metadata for the files in the workflow.
- Set immedate property to true to allow it to open the metadata form as soon as task becomes active
Lock Task
- Attempts to lock all job files associated with a workflow However it can't lock files that are already locked outside the workflow
- Has two transition, i.e. Success (taken when all locks are acquired) and failure (taken when any of the locks can't be acquired) which is required
- Can transfer between task owners for files locked within its own tasks
- Use external task calling unlock.ipl to unlock files
External Task
- Non interactive task that runs as an external application or script on TS server.
- Runs as SYSTEM user on windows OS or runs with userid of the task owner on UNIX server.
- Use the external task to execute unlock.ipl script to unlock files. Unlock.ipl does not acquire any arguments.
- Properties: i) Command - Full path of the executable or script to run ii)Retry - Successive attempts to re-run program again upon failure to start after a specific time whose value can be specified in iw.cfg
- When workflow calls external task program, it passes data as command line arguments, including job and task ID, area vpath and list of job files.
Dummy Task
- A time delay task that transitions to other tasks after some amount of delay time or a specific time
- Use it in a time delay if a lock task fails, before it tries to lock the file again.
- Must have one timeout transition where the timeout transition's time delay can be absolute or relative.
- Any task can use one or more timeout links in addition to any other links.
Update Task
- Used to copy files to another area but only files associated with the job are updated.
- Equivalent to Get Latest if source is a staging area or a Copy To if source is another workarea or an edition
- Area vpath is the destination area
- Properties: i) Delete - propagate deletion of fiels to destiniation area; ii) Overwrite - Overwrite conflicting versions in destination area; iii) Source Area VPath - area from which files are copied
E-mail Task
- Use to send notification to users via email
- Generates a message notifying a user that a task has been assigned to them with information about that job
Special properties:
- Email command: $IW_HOME/iw-perl/bin/iwperl/
- Email body: author_iwmailbody.tpl
- Email body text: author_textbody.tpl
- Email header: author_iwmailheader.tpl
To configure and use email task you must:
- Identify compay'es SMPT server and domain name
- Configure iw.cfg file under [iwsend-mail] section
- Set up an email_map.cfg file in iwhome/local/config/wft/solutions folder
Variables
- Variables allow the job creator to enter workflow or task property values when the job is created
- It can be used as property values for any object types
- There are 7 variable types:
1. Configurable variable: Value entered by the job creator via the form when the job is started. Configurable variables can be local to an object or global to the entire worflow model.
- Use local variables when you want to enable the job creator to select a specific task owner, area vpath or other single property of one task.
- If a value will be used in more than one task, use global property
- To define local configurable variable: Select a task object proeprty->description. Then select "configurable" from variable type drop down list. Enter a label value (will be displayed on the instantiation form). Entering and ID is optional as system will automatically generate a unique ID Recommend leave this default value for local variable. Description field is use for displaying a tooltip help icon. Click OK button
- To define global configurable variable: Select workflow object property->global variable. Then select "configurable" from variable type drop down list. Enter a unique ID value. Enter a label value. Click Add button. When finish click OK button.
2. System variable: Dynamic value which is automatic created and set by the workflow system, when a workflow starts. Can use it as default or property values. All system variable name are uppercase and begin with "$IW_" 
3. Script variable: Variable use to generate a more complex value using JavaScript. Enclose system variable in quotes (e.g. "$IW_USER"). Don't use return to return a value; the script variables value will be the result of the final evaluation i nthe script.
4. Datasource variable: Vaue calculated by an external Java class.
5. Extended attribute variable: Used to set extended attribute data on files.
6. Macro variable: Values used to set extended attribute during workflow.
7. Task variable: Used to pass data along from one task to another task as a job executes.
Resources
For further details, read Workflow Modeler User Guide


No comments:
Post a Comment